The Department of Social Welfare and Development (DSWD) is tasked with uplifting the lives of those who are impoverished or otherwise disadvantaged in Philippine society. To that end, the agency has undertaken various programs and projects over the years, with varying degrees of success. One of its more recent initiatives is the Bottom-Up Budgeting (BUB) Program.
Also Read: List of DSWD Programs and Services for Filipinos
The BUB program was designed to ensure that the country’s budget was focused on the needs of its citizens, rather than on the whims of politicians. It does this by giving communities a say in how government funds are spent. Community members submit project proposals to the DSWD, which are then evaluated by a technical committee. If the proposal is approved, it is then funded by the government.
Contents

What Is BUB Program?
The BUB program is a participatory planning process that engages citizens in identifying development priorities and allocating resources to achieve them. Under the program, community members submit project proposals to the DSWD. These proposals are then evaluated by a technical committee, which consists of representatives from local government, civil society, and academia. If the proposal is approved, it is then funded by the government.
The goal of the BUB program is to ensure that government spending is aligned with citizen priorities. By involving citizens in the budgeting process, it ensures that public funds are spent on projects that will have the greatest impact on people’s lives.
In addition to funding community projects, the BUB program also provides training and capacity-building support to participating communities. This helps ensure that projects are well-planned and well-executed, and that they have sustainable results.
How Does The BUB Program Work?
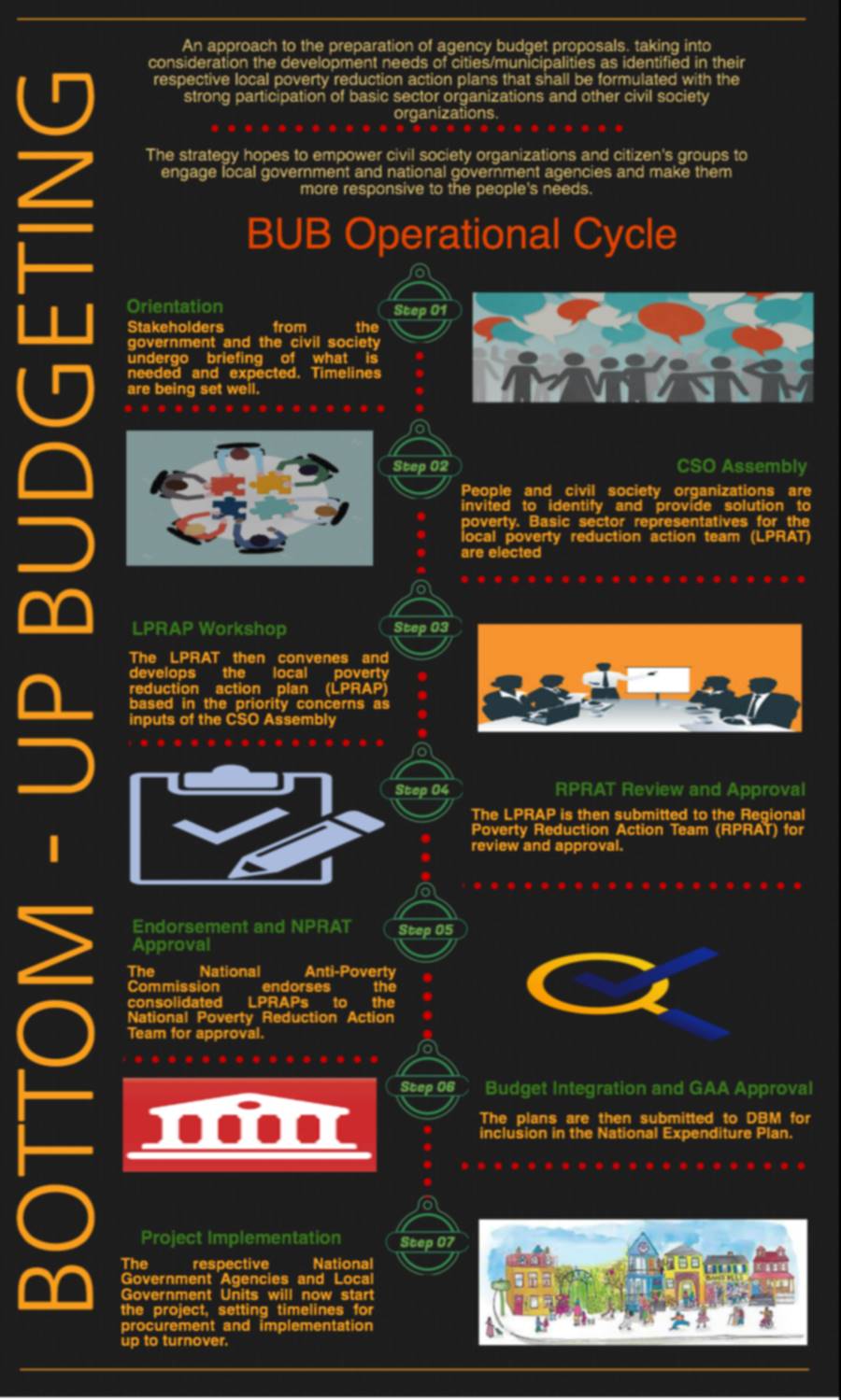
The Municipal/City Development Council will be responsible for preparing the Local Poverty Reduction Action Plan (LPRAP). The LPRAP will be the basis for the Annual Investment Plan (AIP) which will be submitted to the Department of Social Welfare and Development Regional Office.
The AIP will fund priority projects identified by the community that will reduce poverty and improve their quality of life. Some examples of these projects include construction of roads, school buildings, health centers, etc.
Once approved, the funds for these projects will be released to the municipality/city which will then implement the project. The community will be involved in every step of the way – from identifying the problem, to selecting and prioritizing possible solutions, to monitoring and evaluating whether or not the project was successful.
What Is LPRAP In BUB Budgeting
One important component of BUB is the Local Poverty Reduction Action Plan (LPRAP), which is a detailed plan outlining how city governments will use their BUB funds to reduce poverty in their area.
LPRAP Components
As mentioned before, LPRAP consists of four main components: an assessment of poverty, a list of priority programs, a financial plan, and an implementation plan. Let’s take a closer look at each component.
Assessment Of Poverty
The first step in creating an LPRAP is conducting an assessment of poverty in the city. This assessment should include both quantitative and qualitative data on poverty, such as statistics on poverty rates as well as interviews with residents about their experiences living in poverty.
This data will be used to identify the root causes of poverty in the city so that they can be addressed with specific programs and projects.
List Of Priority Programs
Once the root causes of poverty have been identified, city governments must develop a list of priority programs and projects that will address those root causes. These programs should be based on best practices from other cities as well as input from residents about what would work best in their community.
For example, one program might focus on providing job training for residents living in poverty, while another might focus on improving access to healthcare.
Financial Plan
The next step is creating a financial plan for each program or project. This plan should detail how much money will be needed to implement each program as well as where that money will come from. It is important to be realistic in this planning so that you do not overcommit your resources or set yourself up for disappointment if you are unable to raise the full amount of money needed.
Implementation Plan
Finally, you need to create an implementation plan detailing who will be responsible for each program or project and when it will be implemented. This ensures that there is a clear timeline for each program and that someone is accountable for its success. It also allows you to track your progress towards reducing poverty in your city over time.
What are the Benefits of BUB Program
Community Empowerment
The BUB Program gives communities a say in how public funds are spent in their area. This empowers them to identify their own needs and come up with solutions that will work best for them. Furthermore, it builds their capacity to participate in future development planning and budgeting processes.
Improved Service Delivery
By involving communities in the allocation of public funds, the BUB Program ensures that these funds are spent on services that best meet the needs of the people. This results in improved service delivery and more effective use of resources.
Social Inclusion
The BUB Program helps to break down barriers between different social groups and create a sense of ownership and responsibility for local development among all members of the community. This promotes social cohesion and inclusion, which are essential for sustainable development.
Greater Transparency And Accountability
The BUB Program provides for greater transparency and accountability in the use of public funds, as well as improved communication between government agencies and communities. This ensures that resources are used effectively and efficiently, and that corruption is reduced.
Video: Locals Answer: “What Is Bottom-up Budgeting?”
This video is all about DSWD Bottom-up Budgeting in the community. It talks about how the program works and what it can do for the community. Check out these explanations as shared by Filipinos who are more knowledge about the project.
Bottom-Up Budgeting is a participatory approach to budgeting where communities areinvolved in the planning and prioritization of development projects. This allows for a more efficient use of resources as well as improved service delivery. Furthermore, it promotes social inclusion and transparency and accountability in the use of public funds.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What Is A Bottom-Up Approach In Community Development?
The bottom-up approach in community development is a way of working with people and communities to bring about the changes they want to see. It involves empowering individuals and groups to take control of their own lives and work together to create lasting change.
This approach is based on the belief that people are the experts on their own lives and have the power to change their own circumstances. It also recognizes that lasting change is only possible when people are actively involved in the development process.
2. What Are The Characteristics Of Bottom-Up Approach In Community Development?
Typically, the bottom-up approach involves four key steps: needs assessment, planning, implementation, and evaluation. Needs assessment involves gathering information from community members about the problems they face.
Planning involves developing specific goals and objectives for the project, as well as identifying resources and partners. Implementation is when the project is actually carried out. Evaluation takes place after the project is completed, and involves assessing its impact on the community.
3. What Is Bottom Up Economy?
A bottom-up economy is an economic system where organizations and individuals work together to create value. In a bottom-up economy, businesses and individuals are empowered to solve problems and create opportunities. This type of economy relies on collaboration, creativity, and innovation.
Bottom-up economies are often more resilient than top-down economies because they are not reliant on a single individual or organization. Instead, they are built on the strength of the community.
4. How Does Bottom-Up Budgeting Help Communities?
The BUB Program helps communities to participate in the allocation of public funds and to improve service delivery. It also promotes social inclusion and transparency and accountability in the use of public funds. Ultimately, the BUB Program helps to create more sustainable and resilient communities.
5. What Are The Advantages Of Bottom-Up Budgeting?
There are many advantages to the bottom-up approach in budgeting, including improved service delivery, increased transparency and accountability, and greater social inclusion. Additionally, this approach can help to build the capacity of individuals and communities to participate in future development processes.
Summary
The Department of Social Welfare and Development’s (DSWD) Bottom-Up Budgeting (BUB) Program is an innovative approach to poverty alleviation and economic development. The program empowers communities by giving them a direct say in how public funds are spent.
Through a participatory planning process, community members identify their own development priorities and submit project proposals to the DSWD. These proposals are then evaluated by a technical committee, and the most promising projects are funded. While the BUB Program is still in its early stages, it has already had a positive impact on participating communities.
In addition to promoting community empowerment, the program has also helped to increase local government transparency and accountability. With its proven track record of success, the BUB Program is poised to make a lasting difference in the lives of Filipinos living in poverty.